Ventilation
You are here
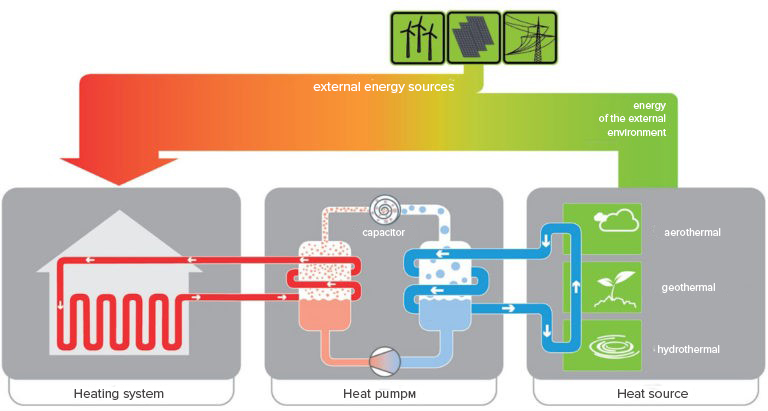
What is a heat pump?

Heat pumps are equipment that, thanks to technology, multiplies the thermal energy of alternative sources (soil, ambient air, groundwater) and transfers it to the heating system.
The sun and air are sources of inexhaustible low-temperature heat. This heat energy is free and renewable.
A heat pump transfers or pumps heat energy from one medium to another. The principle of operation of a heat pump is described later in the article.
In the design of pumps, as well as in refrigeration units, a circuit is used with a refrigerant circulating in it, capable of boiling even with minimal heating. Only the heat pump for heating works as a “reverse refrigerator”.
The work of a heat pump can be divided into 5 stages:
- boiling freon in the evaporator
- refrigerant compression by compressor
- heat transfer from the condenser to the heating circuit
- passage of the cooled condensed refrigerant through the throttle valve
- return of cooled and liquid freon to the evaporator heat exchanger
Heat pumps are intended for heating and cooling. An additional function is to heat water for domestic or industrial use. This is the most functional equipment in comparison with any boilers or air conditioners.
The heat pump works very economically, because it consumes energy only for the operation of the compressor and circulation pumps. The energy efficiency of heat pumps is very high. The energy conversion factor reaches 4-6 and even higher. This means that every kilowatt of energy used is converted by a heat pump into 3-5 kilowatts of heat, which is used to heat a house or to heat water.
You will have to pay several times less for heating a house or heating water than if an electric boiler or a boiler were used. Heating costs can be saved up to 75-80%!
Under current gas tariffs, a gas boiler is 2-3 times more expensive to operate than a heat pump.
Heat can be extracted from:
- groundwater table at a depth of 15-20 m;
- a nearby body of water;
- soil pads with a horizontal collector laying depth up to 1.2-1.5 m;
- deep drilled wells up to 40-50 m deep.
There are many more ways to use heat pump technology to reduce heat loss and reduce heating costs.
For example, when using excess heat from technological processes, waste water heat, and in many other cases.
There are systems that use geothermal heat, heat from the air, or installations that extract hydrothermal heat. Let’s highlight several main types of heat pumps.
A ground source heat pump is a system that draws excess heat from a layer of surface soil, deep boreholes or a nearby body of water.
The ground temperature at a depth below the layer freezing in winter is always positive – up to 5-10 (° C). The heat accumulated during the summer is sufficient for the ground source heat pump to heat the room in winter.
For heat removal, a tubular plastic collector is laid or double probes are lowered, in which a coolant circulates, which does not freeze in winter conditions. The more living space, the longer the collector pipes or the depth of the probes. The specific heat removal power for different soils can vary from 8 to 32 W / m². The characteristics of the soil and its layers are also taken into account, which requires geological surveys.
If there is a pond or reservoir near the house with a sufficient volume of water and depth, spirals and rings of a plastic collector are placed into it to the depth (to the bottom).
The water-to-water heat pump, the principle of which is based on the extraction of heat from groundwater, is rather complicated to install. The water temperature at the depth is constant throughout the year – about + 10 ° С.
To install such a heat pump, an analysis of the depth of the water horizon, quantity, quality and purity of water is required. Its performance in terms of heat or cold does not depend on atmospheric conditions or the change of season. The energy conversion ratio of the water heat pump is high – COP up to 5 and higher, but installation and maintenance are problematic.
A water-to-water heat pump for heating is a profitable option only under the condition of competent selection and calculation of equipment, as well as highly qualified installation and commissioning.
The price of geothermal and water heat pumps is high due to the need for preliminary surveys and expensive installation work.
Such a heat pump is more affordable in terms of price and installation. It is most suitable for integration into a modernized heating system, and is also easy to install and quickly pays for itself when introduced in a new home. Since its thermal performance depends on the outside air temperature, it is advantageous to use an air heat pump in bivalent circuits, with a backup second heat source.
The total capacity of a heat pump with a backup source becomes almost half as much as its cost, but the energy efficiency and economy of the overall heat supply system remains optimal.
Distinguish between a monoblock layout or a kit that includes outdoor and indoor units. The inverter air source heat pump responds precisely and economically to priority loads for heat, hot water or cold. The energy efficiency coefficient of such systems is up to 5 or more, they are able to operate even at outdoor temperatures down to -25 ° C. These are the most popular heat pumps for use in temperate climates in most of the territory of Ukraine.
Such models are an option available in terms of climatic conditions for a quickly payback project for the modernization of heating or installation in a new house both in cities with millionaires and in the regions.
An excellent example of an air-to-water heat pump is the Arctic Home Basic and Arctic Home Smart series, high-performance equipment from the British brand Mycond.
Using heat from ventilation or outdoor air, an air-to-air heat pump is similar in terms of the operation for a cooling / heating air conditioner, but with a priority of work on heating. This heat pump is used as a system that allows you to save money on heating your home not only in Europe, but also in Ukraine.
In addition, such heat pumps can be equipped with a set for preparing hot water and are distinguished by high rates of seasonal energy efficiency.
There are also other schemes of heat pump systems:
- ground-air heat pump;
- brine-water heat pump;
- others.
Heat pumps are used to heat water in swimming pools or technological processes, in some industrial areas or in construction for heating any commercial facility.
- Innovative technologies for heat supply, air conditioning and hot water supply, presented in one device – a heat pump.
- Economical and several times lower costs for heating and hot water supply.
- Environmentally friendly heat pump, no CO2 emissions and environmental pollution.
- Fire safety, no need for supervision, approval, constant monitoring of equipment safety.
- Intelligent control and economical operating modes, microclimate control by temperature and humidity sensors.
- Control of different temperature heating circuits: radiators and underfloor heating.
- Air conditioning and heating with heat pumps and fan coil units.
- A ground source heat pump, the price of which is high, is an economically viable option for heating a new house without gas, especially in conditions of limited power supply for the house.
Only highly qualified specialists can choose the right set of heat pump equipment that works according to one or another scheme, with reference to a specific section of a private house, taking into account engineering systems and building planning.
Correct calculations determine: the cost of the system, its efficiency and reliability. Heat pumps are innovative systems with complex installation and intelligent control. To implement such projects, it is necessary to turn to professionals in order to choose the most suitable set of equipment in terms of power and price and calculate the economic benefit from its implementation.